ProfessionalCommunity Edition
Enumerating usernames with Burp Suite
-
Last updated: March 1, 2024
-
Read time: 2 Minutes
You can use Burp Intruder to insert a list of possible usernames into an authentication mechanism, such as a login form or registration form. This enables you to identify valid usernames that can be used in other attacks. For example, using a list of enumerated usernames greatly reduces the time and effort required to force a login in a password-guessing attack. It can also be used for attacks on user data or sessions.
Steps
You can follow along with the process below using our Username enumeration via subtly different responses lab. If you're using the lab, make sure you use the list of usernames included in the lab instructions.
You can use Burp Intruder to enumerate usernames:
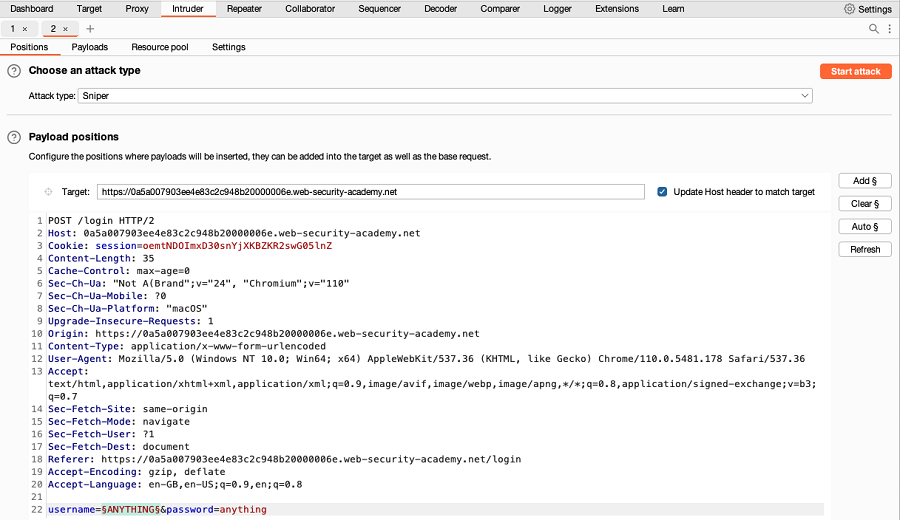
- Identify a failure message for a username-based authentication mechanism. In the message, highlight the username value, right-click and select Send to Intruder.
-
Go to Intruder > Positions. Notice that the username value has been automatically added as a payload position.
-
Go to the Payloads tab. Under Payload settings [Simple list] add a list of usernames that you want to test.
- If you're using Burp Suite Professional, you can open the Add from list drop-down menu and select the Usernames list.
- If you're using Burp Suite Community Edition, manually add a list of usernames.
- Go to the Settings tab. Under Grep - Match, select Flag result items with responses matching these expressions. When you start the attack, Intruder identifies messages that include the expressions in the list. You can use the default list of expressions or add your own.
-
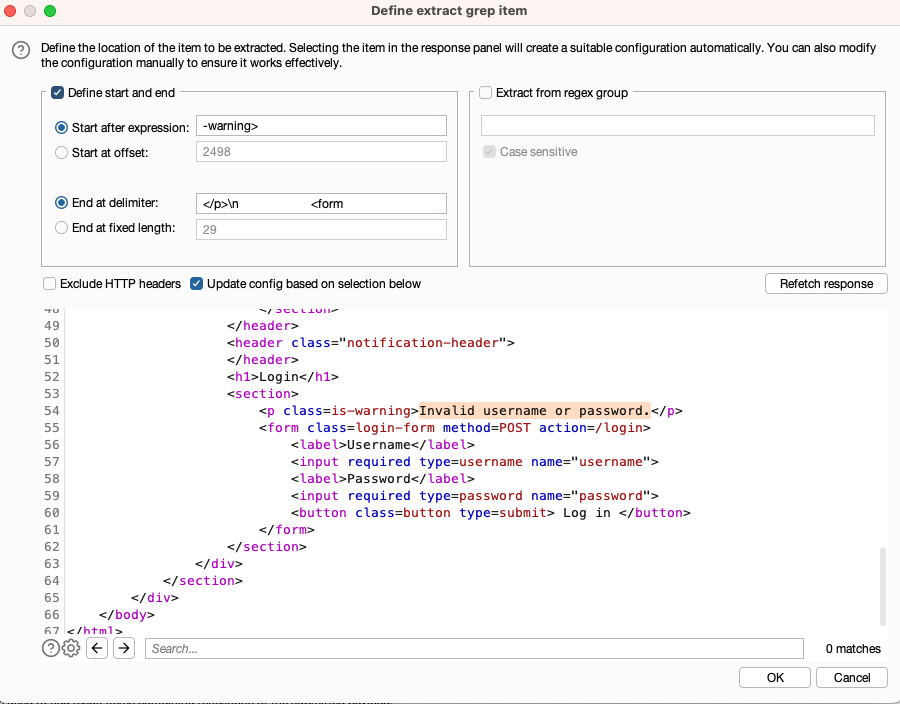
Add an extract grep for sections of interest in the response.
- Under Grep - Extract, select Add. The Define extract grep item dialog opens.
- Highlight the section in the response that you want to extract, such as an error message.
- Press OK. The item is added to the list. When you start the attack, Intruder extracts the text at this location in each response and display it on the results table.
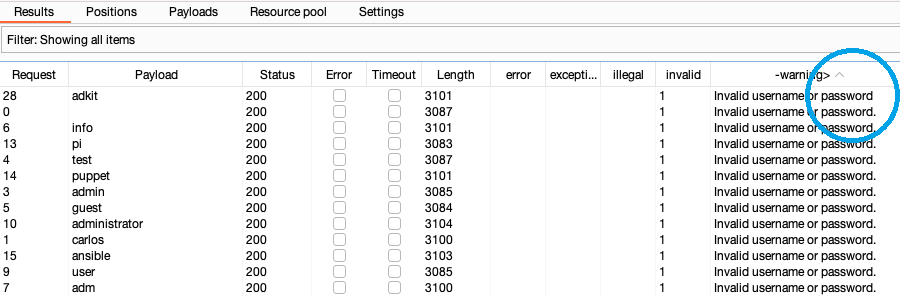
- Click Start attack. The attack starts running in the new dialog. Intruder sends a request for each username in the list.
-
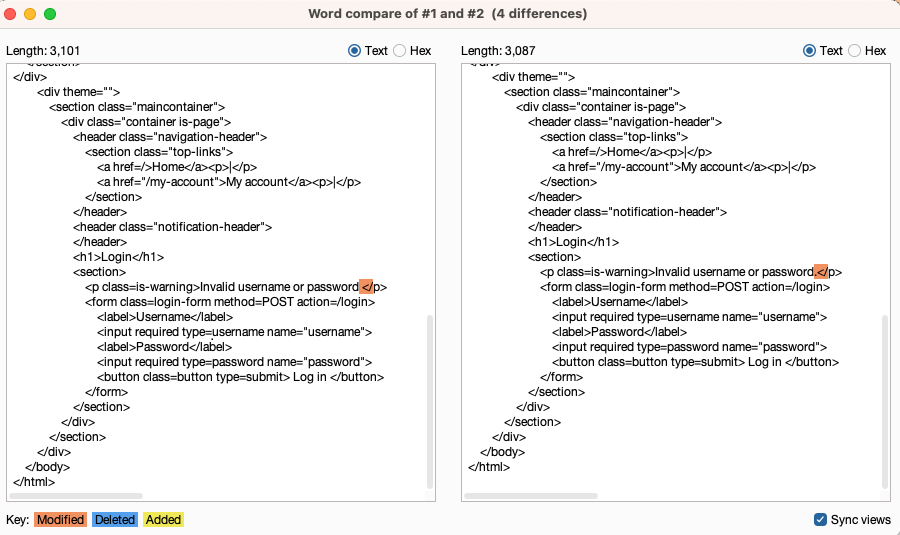
When the attack is finished, study the responses to look for any behavior that may indicate a valid username. For example, look for any anomalous error messages, response times, or status codes. In the example below, one error message is missing a full stop.
- To investigate the contents of a response in detail, right-click and select Send to Comparer (response). Do the same for the original response.
-
Go to the Comparer tab. Select the two responses and click Words or Bytes to compare the responses. Any differences are highlighted.