We take a look back at some of the latest offensive security tools that were launched over the past three months

Hacker Summer Camp dominated the release of new hacking tools in the past quarter, despite the coronavirus pandemic forcing both events online.
Black Hat USA saw a plethora of offensive tools demonstrated including an open source project aimed at scanning for Kubernetes vulnerabilities and a utility to automate silent remote code execution (RCE) attacks on unsuspecting Windows devices.
Meanwhile, DEF CON saw its usual crowd of hacking enthusiasts attempt to compromise a Tesla in the Car Hacking Village.
Here’s our roundup of the latest hacking tools for the third quarter of 2020.
Vimeo’s Psalm security tool expanded to support taint analysis
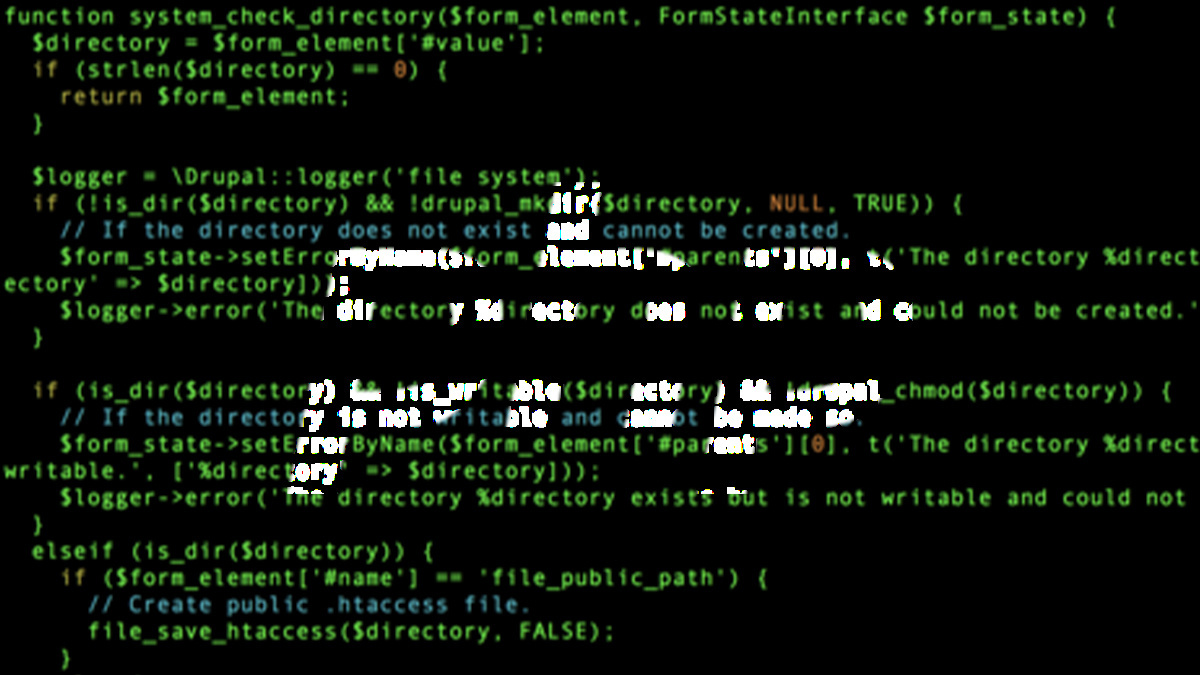
Psalm, Vimeo’s open source static analysis tool for PHP applications, was expanded to support taint analysis.
Taint analysis enables developers to check the flow of user input in application code and determine whether ‘tainted’ input can compromise the program.
The tool looks for possible cross-site scripting (XSS) and SQL injection bugs related to user input sources. Users can also define their own custom taint sources.
In addition, it is configured to reduce the number of false positives after the security team at Vimeo found that commercial tools of this kind produced too many.
Read more about Psalm’s taint analysis tool
The Pwning Machine – a new bug bounty testing environment from YesWeHack

YesWeHack, Europe’s largest bug bounty platform, launched a Docker-based pwning environment equipped with an “all-in-one, customizable, and extensible suite of tools”.
Dubbed The Pwning Machine, it includes a DNS server, HTTP router, web server, and pipeline runner.
The environment was designed for use by bug bounty hunters, and was developed to simplify the process of finding vulnerabilities, says YesWeHack.
Read more about The Pwning Machine
KubiScan: Open source Kubernetes security tool showcased at Black Hat 2020

Open source tool KubiScan can enable cluster administrators who orchestrate containerized environments with Kubernetes to shrink their attack surface.
KubiScan was unveiled at this year’s virtual Black Hat USA conference. It can scan for pods that contain privileged service account tokens, which can be abused to launch privilege escalation attacks or to compromise the cluster.
Administrators often manage large environments with more than a thousand containers, explained Eviatar Gerzi, meaning it is easy to lose control of each one.
“Tools like KubiScan provide a good picture of the particular containers that are the most vulnerable,” he explained.
ATTPwn: Adversary emulation tool allows pen testers to spot security holes before attackers

Another tool to be unveiled at Black Hat USA was designed to emulate adversaries conducting malware campaigns or probing networks for secrets.
ATTPwn aims to enable penetration testers to identify potential weaknesses impacting an organization, based on techniques and tactics set out in the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
Built for use on Windows machines, it can emulate well-known attacks such as the WannaCry and NotPetya ransomware campaigns.
The tool’s creators said it can also be used to test networks against established vulnerabilities.
Open source post-exploitation framework automates silent RCE attacks on Windows devices

AutoRDPwn is a post-exploitation framework that allows security pros to recreate shadow attacks against Microsoft Windows systems.
A shadow attack is the term given to the abuse of misconfigured shadow sessions, explained Joel Gàmez, who built the PowerShell tool, at Black Hat USA.
It can allow a remote actor to view the desktop of their victim, and even control it on demand, using native tools of the operating system itself.
There are no obvious warning signs that AutoRDPwn has been deployed – it does not consume a suspicious amount of computer resources, and the victim cannot tell if someone is watching in real time, meaning RCE attacks can go unnoticed.
xGitGuard uses AI to detect inadvertently exposed data on GitHub

A tool to detect credentials and other secrets accidentally exposed on GitHub was also demonstrated at the Black Hat online event.
Dubbed xGitGuard, it uses artificial intelligence (AI) to dig out API tokens or user credentials often mistakenly left in code on the open source platform.
Its creators said the utility offers a quick, scalable way to scan for such information by utilizing machine learning.
Low hanging ‘Forbidden’ fruits: Post-compromise tool targets unguarded Magento flank

Security researchers discovered a post-compromise tool attacking Magento-powered websites that can enable attackers to view orders, gain administrative access, and create additional backdoors.
Called Forbidden, it is also effective at concealing telltale indicators of compromise, meaning an attack can go unnoticed by the victim.
The dump function acquires the configuration file and database configuration information including admin username, email address, and the password hash. Attackers can also access the encryption key used by Magento for encrypting store data.
Forbidden can be used in both Magento 1 and Magento 2 environments.
Other hacking tools news this month
This month has also seen the release of a number of defensive tools aimed at improving security for both organizations and computer users:
- A new open source browser extension dubbed Behave! aimed at improving users’ security and privacy by detecting port scanning, access to private IPs, and DNS rebinding in Chrome and Firefox, was released.
- Microsoft Research launched a free service called Project Freta designed to detect the presence of rootkits and advanced malware in the memory snapshots of live Linux systems.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) launched a new tool – HTTP Desync Guardian – designed to “analyze HTTP requests to prevent HTTP desync attacks, balancing security and availability”.
- The University of Iowa, Mozilla, and the University of California, unveiled FP-Inspector, which uses a syntactic-semantic approach to detect fingerprinting scripts, using machine learning models based on static and dynamic JavaScript analysis.
- And SANS Institute collated a list of all the free tools its instructors have developed, published via Twitter.
READ MORE Black Hat USA: Your guide to the top web hacking sessions in 2020






