ProfessionalCommunity Edition
Working with GraphQL in Burp Suite
-
Last updated: January 30, 2026
-
Read time: 2 Minutes
GraphQL is an API query language that is designed to facilitate efficient communication between clients and servers. It enables the user to specify exactly what data they want in the response, helping to avoid the large response objects and multiple calls that can sometimes be seen with REST APIs.
GraphQL services are commonly used in authentication and data retrieval mechanisms. This means that if an attacker can successfully send malicious requests, they may be able to access vulnerable information or even execute higher-severity exploits such as cross-site request forgery (CSRF).
Burp Suite makes it easy to construct GraphQL requests and learn more about a GraphQL API's schema.
Read more
For a full primer on what GraphQL is and how it works, see Web Security Academy: What is GraphQL?.
Viewing and modifying GraphQL requests
If Burp detects a GraphQL request, it automatically adds a GraphQL tab to the message editor for the request. This tab separates the GraphQL query from the rest of the request, and formats it in a way that makes it easy to view and edit the query structure (displayed in the Query panel) and its associated variables (displayed in the Variables panel).
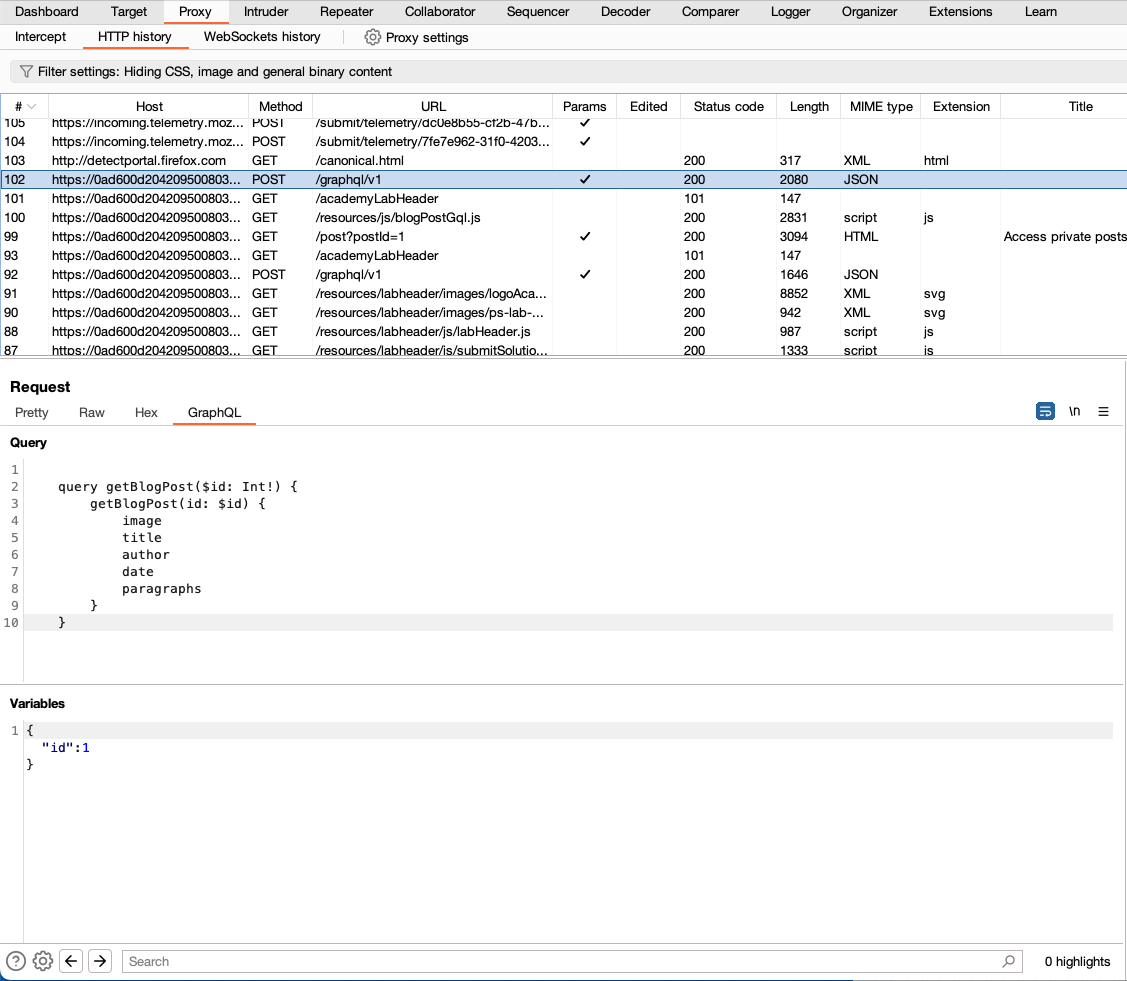
Accessing GraphQL API schemas using introspection
Introspection queries can return information about a GraphQL schema, such as the queries and mutations that are supported by the API. This information is extremely useful when planning how to attack an API.
Burp can generate introspection queries for you to send to your target application. The data returned in the response can be used to identify how to test your target application's GraphQL API for vulnerabilities.
To run introspection:
-
Browse the target application, looking for requests to a GraphQL endpoint.
GraphQL services often use similar endpoint suffixes. Look for queries to the following locations:
/graphql/api/api/graphql/graphql/api/graphql/graphql
These endpoints may also contain a version number as a suffix, for example,
/graphql/v1. - Right-click the GraphQL request, then select Send to Repeater.
- In Repeater, right-click anywhere within the Request panel of the message editor, then select GraphQL > Set introspection query to insert an introspection query into the request body.
-
Click Send.
If introspection is enabled, the server should return the full schema of the GraphQL API in its response to your introspection query.
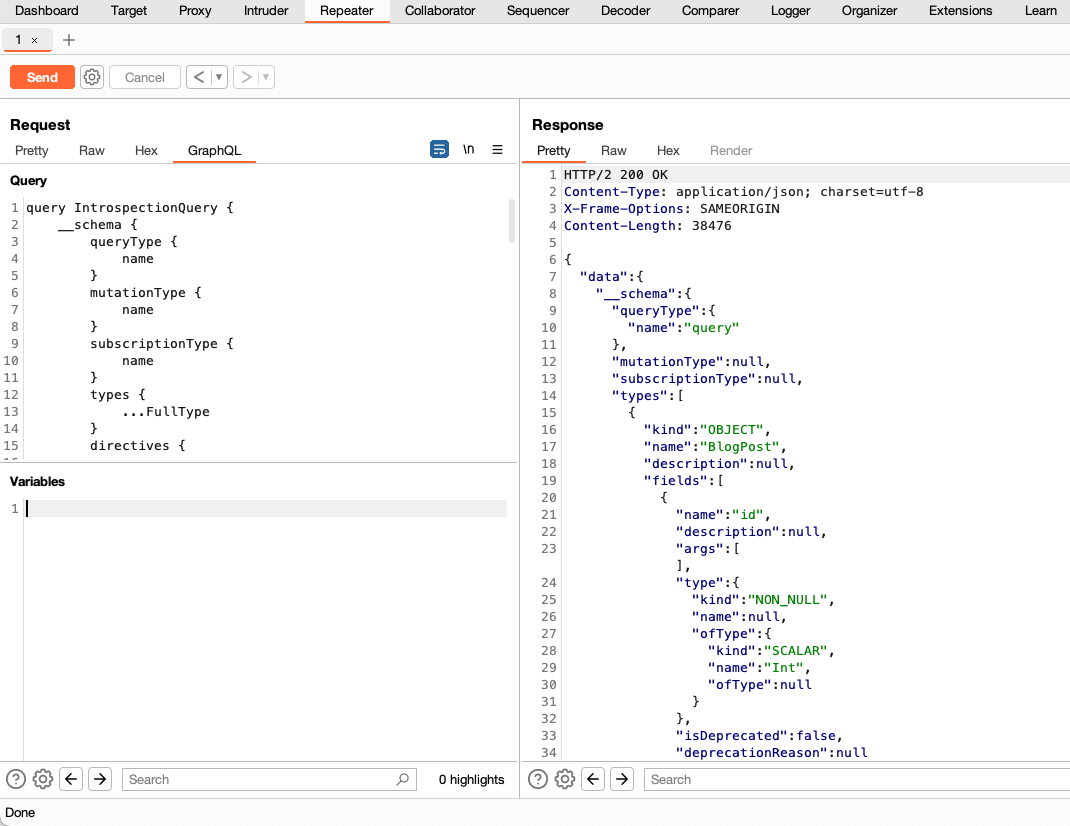
This introspection query works with most GraphQL servers. However, if you are working with an older GraphQL server, it may fail. If that happens, right-click anywhere within the Request panel of the message editor, then select GraphQL > Set legacy introspection query and try again.
-
Right-click anywhere within the Response panel of the message editor, then select GraphQL > Save GraphQL queries to site map.
Each of the available queries that Burp discovered during introspection is saved as a node on the site map. You can examine these queries to find one that you want to investigate further, and send them to Intruder or Repeater to start your attack.


